Mar
11th
Stay connected Subscribe to our RSS feed
In today's world, automakers are trying harder than ever to clean up their act by developing alternative power sources for their vehicles that aren't internal combustion engines. Electric motors have been around for nearly 200 years. Present in our day-to-day lives, this technology has evolved and has now found its way into certain vehicles.
It's a simple concept
Electrical energy transforms into mechanical energy by transmitting an electrical current to coil windings that, in turn, become electromagnets. A rotating force is thus created by the opposing forces from either pole. Identical charges oppose each other while opposite charges attract each other.
Let's find out more
The majority of electric motors are comprised of a rotor and a stator.
The stator is the rigid exterior part fitted with magnets or electromagnets. The rotor is the rotating part inside the stator, fitted with permanent magnets or electromagnets whose charge is determined by the direction of the electrical current. The rotor is either pushed away or attracted by the magnets mounted on the stator, which in turn creates a rotating movement.
This rotating movement is transferred to a transmission shaft in order to obtain mechanical energy. The voltage, amperage, and electromagnetic force determine the rotational speed of the shaft. There are different types of electric motors, some favour torque while others are more durable or precise.
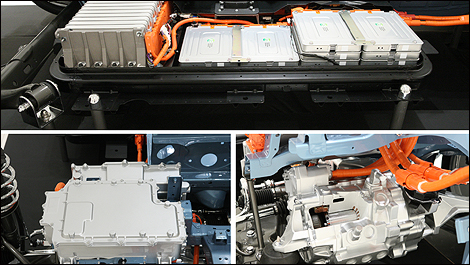
The electricity that is applied to the electromagnets is produced by batteries which convert chemical energy into electrical energy. On-board computers and controllers are the bridge between the battery and the electric motor.
There are a number of different batteries on the market. Some are designed to store energy for long periods of time while slowly delivering the power, while others are capable of supplying huge bursts of energy in a very short time.
Batteries
Here is a list of the most popular batteries currently on the automotive market.
Acid wet batteries
This is the battery type most often found in 12-Volt systems and is made of a series of six galvanized cells. Nowadays, these batteries are commonly used to power accessories and to start internal-combustion engines.
Nickel metal hydride
These rechargeable batteries require minimal maintenance, but are sensitive to extreme temperature gaps. They are mostly used because of their dependability and low cost. These batteries are the same variety as those found on the Toyota Prius and Lexus CT200h.
Lithium-ion
This is the most advanced automotive-used battery, and they are also very popular in portable computers. They are 20%-35 % lighter and smaller than equivalent nickel metal hydride batteries. A big negative for lithium-ion batteries is that they are highly flammable. Security systems have been developed in order to avoid problems that may arise from collisions. They are also very expensive.
Charging
There are two ways to recharge the batteries found in the majority of vehicles currently on the market. They can either be plugged into a 110- or 220-Volt power source, or they can be recharged by recuperating the kinetic energy from the car's braking system. The electric motor acts like an alternator, thus capturing the energy created by the turning wheels, which is also used to slow the car down.
 |
| Photo: Nissan |
It's a simple concept
Electrical energy transforms into mechanical energy by transmitting an electrical current to coil windings that, in turn, become electromagnets. A rotating force is thus created by the opposing forces from either pole. Identical charges oppose each other while opposite charges attract each other.
Let's find out more
The majority of electric motors are comprised of a rotor and a stator.
The stator is the rigid exterior part fitted with magnets or electromagnets. The rotor is the rotating part inside the stator, fitted with permanent magnets or electromagnets whose charge is determined by the direction of the electrical current. The rotor is either pushed away or attracted by the magnets mounted on the stator, which in turn creates a rotating movement.
This rotating movement is transferred to a transmission shaft in order to obtain mechanical energy. The voltage, amperage, and electromagnetic force determine the rotational speed of the shaft. There are different types of electric motors, some favour torque while others are more durable or precise.
The electricity that is applied to the electromagnets is produced by batteries which convert chemical energy into electrical energy. On-board computers and controllers are the bridge between the battery and the electric motor.
There are a number of different batteries on the market. Some are designed to store energy for long periods of time while slowly delivering the power, while others are capable of supplying huge bursts of energy in a very short time.
Batteries
Here is a list of the most popular batteries currently on the automotive market.
Acid wet batteries
This is the battery type most often found in 12-Volt systems and is made of a series of six galvanized cells. Nowadays, these batteries are commonly used to power accessories and to start internal-combustion engines.
Nickel metal hydride
These rechargeable batteries require minimal maintenance, but are sensitive to extreme temperature gaps. They are mostly used because of their dependability and low cost. These batteries are the same variety as those found on the Toyota Prius and Lexus CT200h.
Lithium-ion
This is the most advanced automotive-used battery, and they are also very popular in portable computers. They are 20%-35 % lighter and smaller than equivalent nickel metal hydride batteries. A big negative for lithium-ion batteries is that they are highly flammable. Security systems have been developed in order to avoid problems that may arise from collisions. They are also very expensive.
Charging
There are two ways to recharge the batteries found in the majority of vehicles currently on the market. They can either be plugged into a 110- or 220-Volt power source, or they can be recharged by recuperating the kinetic energy from the car's braking system. The electric motor acts like an alternator, thus capturing the energy created by the turning wheels, which is also used to slow the car down.
 |
| Photo: Michel Deslauriers |
 The latest auto news, reviews, prices, product and vehicle releases.
The latest auto news, reviews, prices, product and vehicle releases.